The Panera Bread cybersecurity breach disclosed in January 2026 exposed millions of customer accounts and prompted multiple lawsuits, intensifying scrutiny of corporate data-protection practices in the restaurant industry. The U.S. fast-casual chain confirmed attackers accessed personal customer information, and plaintiffs now allege the company failed to provide adequate safeguards to protect consumer privacy.
Table of Contents
Panera Bread Confronts Lawsuit Fallout
| Key Fact | Detail / Statistic |
|---|---|
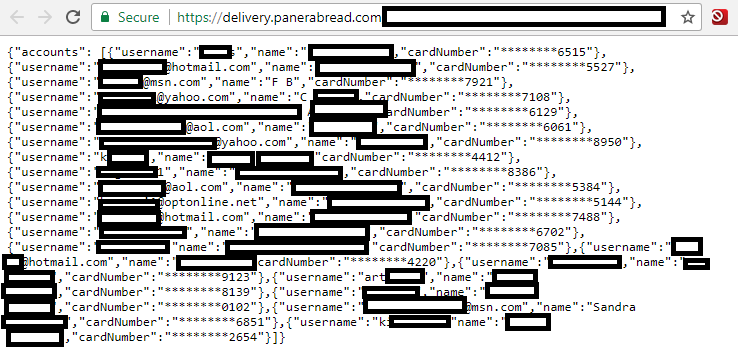
| Accounts affected | About 5.1 million customer records |
| Data exposed | Names, email addresses, phone numbers, and addresses |
| Legal action | Multiple class-action lawsuits filed |
Court proceedings are expected to continue through 2026. Privacy advocates say the outcome could influence how restaurant chains handle digital accounts and loyalty programs. As one cybersecurity researcher noted, “Data protection is no longer optional — every consumer-facing company now operates in a security-critical environment.”
What Happened in the Panera Bread Cybersecurity Breach
Security researchers say hackers infiltrated the company’s customer account database connected to its online ordering and rewards program. Attackers copied personal contact information tied to user profiles.
The company confirmed unauthorized access to customer data but reported that financial payment card information was not compromised. Instead, exposed records included identifying information such as names, email addresses, phone numbers, and home addresses.
Cybersecurity analysts warn this information still presents serious risks.
“Contact data allows criminals to craft believable messages that appear to come from trusted businesses,” said a breach-response consultant who advises retailers after cyberattacks. “Victims are more likely to respond because attackers already know who they are.”
Investigators believe the attackers exploited authentication weaknesses and automated account-access tools commonly used in modern cybersecurity breach incidents.
How Loyalty Apps Became a Target
Restaurant apps have become lucrative targets for hackers because they collect large volumes of personal data. Loyalty programs store email addresses, purchase histories, and contact details to offer promotions and delivery services.
Cybersecurity researchers note that restaurants historically focused more on payment protection than broader customer data security. As digital ordering expanded after the pandemic, data collection increased faster than security investments at some companies.
“Food service companies are now technology companies whether they planned to be or not,” said a technology policy analyst who studies digital commerce risks. “They operate mobile platforms, databases, and customer analytics systems just like banks and retailers.”
Lawsuits and Legal Allegations
Class-Action Claims
Within weeks of the disclosure, customers filed several data breach lawsuit complaints in federal court. Plaintiffs argue the company failed to use industry-standard security protections and did not notify customers quickly enough.
The lawsuits claim affected individuals now face an elevated risk of fraud, phishing attacks, and identity theft.
Legal filings assert the company stored sensitive personal information but did not adequately encrypt or protect it. Plaintiffs also seek compensation for time spent monitoring accounts and mitigating risks.
Prior Incident Increases Legal Pressure
The new litigation follows a previously disclosed 2024 security incident involving employee-related records. That case resulted in a financial settlement and credit monitoring for affected individuals.
Attorneys say the earlier breach may influence the court’s evaluation.
“When a company has experienced a previous cyberattack, judges often ask whether reasonable improvements were implemented afterward,” said a privacy law attorney specializing in consumer protection.
Why Customers Are Concerned
Even without credit card numbers, personal data exposure creates real-world risks.
Criminals commonly use stolen information to:
- send fraudulent emails posing as restaurant order confirmations,
- impersonate delivery drivers or customer support,
- attempt password resets on other websites.
Many scams rely on familiarity. A message referencing a real restaurant brand appears more credible to recipients.
Because many consumers reuse passwords, attackers often test stolen email credentials across unrelated services — a technique known as credential stuffing.
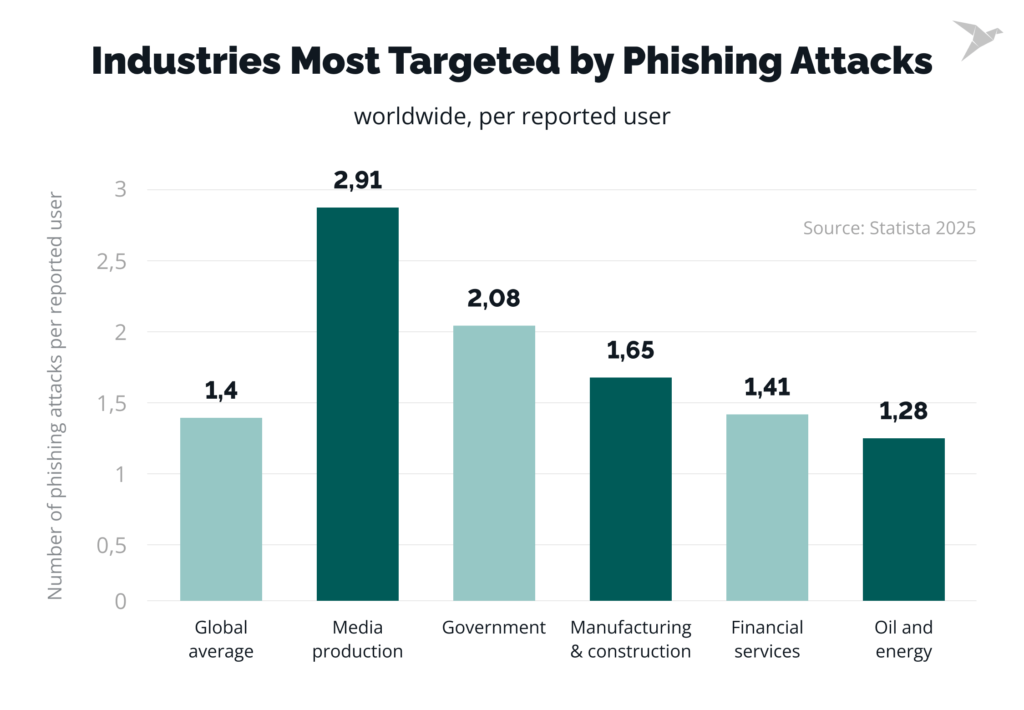
The Economic Impact of a Cybersecurity Breach
Beyond customer risks, cybersecurity experts say breaches can impose significant financial damage on companies. Costs often include:
- forensic investigations
- legal defense
- regulatory fines
- customer notifications
- security upgrades
- reputational loss
Industry research groups estimate that reputational harm can exceed direct legal expenses. Consumers may reduce app usage or delete accounts after a breach.
“Trust is a currency in digital commerce,” said a retail technology consultant. “Customers may forgive service delays, but they rarely ignore privacy concerns.”
Company Response and Security Measures
The company said it secured its systems after detecting suspicious activity and required password resets for certain users. It also strengthened monitoring tools and authentication protections.
Security professionals stress that immediate response reduces harm.
“Rapid containment and transparency are critical after a breach,” said a digital risk analyst. “The faster users are informed, the less time criminals have to exploit the information.”
What Customers Should Do
Consumer-protection agencies recommend affected users:
- Change passwords immediately
- Enable two-factor authentication
- Monitor suspicious emails and texts
- Avoid clicking unexpected delivery notifications
- Review bank and online accounts regularly
Experts also advise using unique passwords through password-manager software.
Regulatory and Privacy Implications
The breach highlights a broader policy issue: companies increasingly hold personal data traditionally associated with financial institutions.
In the United States, privacy laws vary by state, though states such as California require companies to notify consumers of breaches involving personal information. Regulators may examine whether organizations followed reasonable security practices.
European regulators enforce stricter rules under the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), which can impose large penalties for failing to protect consumer information. While the incident occurred in the United States, international users could still be affected.
Privacy advocates say restaurant apps represent a regulatory gap.
“These programs collect behavioral data, purchase patterns, and location details,” said a digital privacy researcher. “Consumers often do not realize how much information is stored.”
Broader Context: Rising Attacks on Retail and Hospitality
Cyberattacks against retailers and restaurants have increased worldwide. Criminal groups target companies that handle large customer volumes but may lack bank-level cybersecurity infrastructure.
Restaurants increasingly rely on:
- mobile ordering
- third-party delivery integrations
- cloud-based point-of-sale systems
Each connection creates a potential entry point for attackers.
Security specialists warn that businesses transitioning to digital platforms must adopt enterprise-level defenses, including multi-factor authentication, encryption, and real-time intrusion detection.
What Happens Next
Federal courts will determine whether the lawsuits can proceed as class actions. That decision often influences whether cases settle or move toward trial.
Legal analysts say similar cases typically end in settlements including identity-protection services and financial compensation.
Regulators may also examine the incident to assess whether data-protection standards were adequate.
FAQs About Phishing Attack Impact
Was payment card information stolen?
No evidence indicates credit or debit card numbers were compromised.
Why is personal contact data valuable?
It allows targeted scams, phishing messages, and impersonation attempts.
Could international users be affected?
Yes. Anyone who created an account or used the mobile app may be included.
Should customers delete their account?
Security experts generally recommend updating passwords and enabling authentication before deciding.